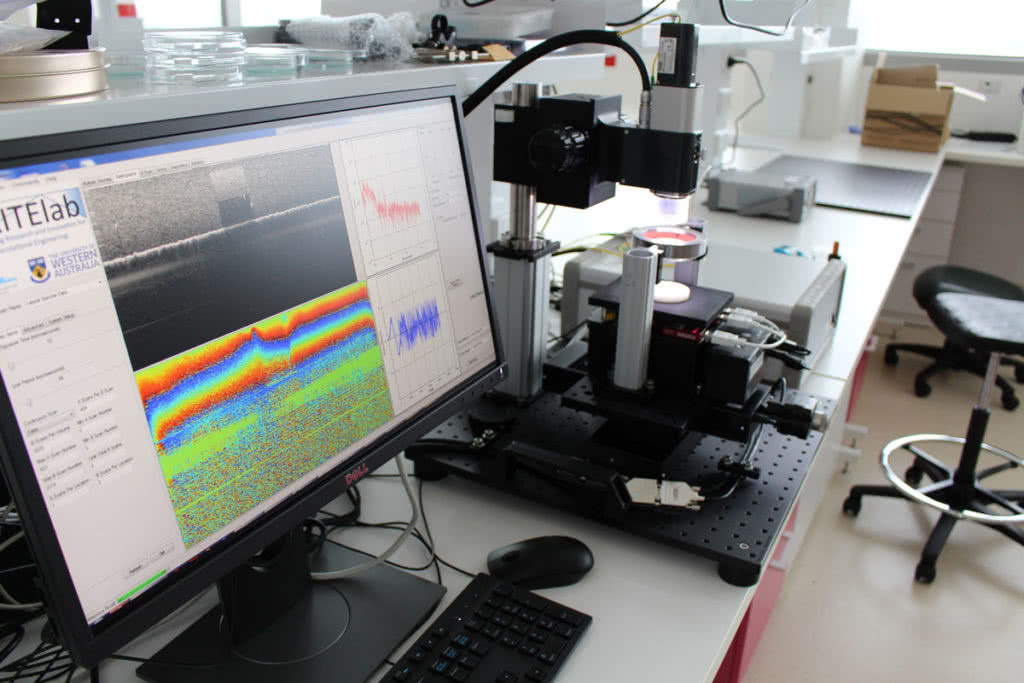
In this Medical Case Study, all information and images were kindly provided by Phd Researcher Wes Allen from the University of Western Australia, BRITElab at Harry Perkins Institute of Medical Research. Futek’s Jnr S Beam Load Cells are part of the process.
Breast cancer has the second highest mortality rate of cancers in females. Firstly, Breast-conserving surgery is the most common surgical procedure. Used in the treatment of early stage breast cancer. The aim of this surgery is to remove all malignant tissue surrounded by a ‘margin’ of healthy tissue. Malignant tumours within the margin indicates a higher rate of re occurrence of cancer. Therefore, as a result the patient may undergo a second surgery. Currently, 20–30% of patients undergoing breast-conserving surgery require additional surgeries.
Compression optical coherence elastography is a high resolution optical imaging technique that probes the mechanical properties of tissue. The technique can identify regions of malignant tumour by generating three-dimensional images of tissue elasticity.
The Medical Case Study Process
Firstly, the bench-top system with a motorised lab jack applies a bulk preload to the tissue. Elastography is conducted. Biological tissues, including human breast tissue, exhibit nonlinear stress-strain relationships. Secondly, in order to be able to perform intra- and inter-specimen comparison of elasticity. The bulk preload and resulting applied force must be considered. FUTEK miniature s-beam load cells are mounted onto the motorised lab jack.
Therefore, after publishing a number of studies on the feasibility of the technique. The BRITElab group are embarking on a larger scale clinical study to determine the sensitivity and sensitivity of the technique for clinical assessment of tumour margins. Finally, their vision is that this technology will be used in surgery theaters around the world in the future. In conclusion, reducing the number of additional surgeries required.
For more information on this medical case study, contact us.