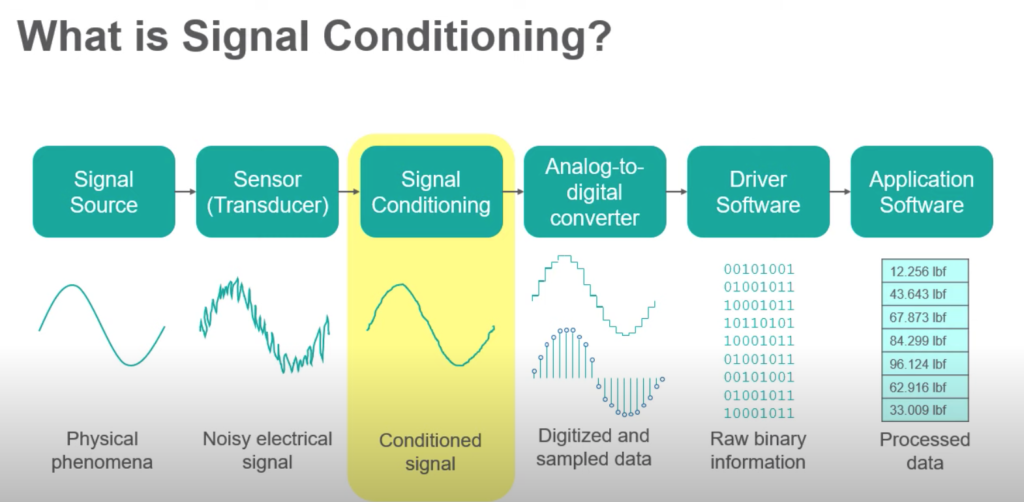
Signal Conditioning – What is it & How does it work?
Signal conditioning is the manipulation of a signal. It prepares signals for the next stage of processing. Signal conditioners convert or “clean” signals so a DAC device can read a signal’s data. Although often overlooked, this is one of the most important steps in data processing because it allows conventional instruments process difficult-to-read signal data.
Why is Signal Conditioning Required?
It’s important to optimise signals for data processing. You can’t rely on the accuracy of a signal measurement without optimising it first. Furthermore, signals collected off sensors aren’t usually in the right format. Some signals also contain unwanted noise. Both these things can comprise signal data.
Types of Signal Conditioning
- Amplification: Increases the input signal amplitude for low voltage output signals. This process allows amplifiers to increase the resolution of a signal.
- Attenuation: This process decreases the input signal amplitude. For example, if an output voltage is more than 10 volts this process decreases the output to fall into the correct range for a DAC device.
- Filtering: This process rejects unwanted noise within a certain frequency range. This is especially useful in removing frequency ranges or bands from vibration measurements.
- Excitation: Some sensors require an excitation or power source to operate. These include strain gauges, and thermistors. Signal conditioning modules provide these signals through the a process called excitation.
- Linearisation: This is for signals that do not show a linear relationship to the actual measurement. It charts the input signal voltage from the sensor against the corresponding value of the physical measurement.
- Bridge Completion Isolation: This helps protect sensitive equipment from potential hazards that come through the signal path from the sensor. An Isolator filters out unwanted noise along the signal path. It also eliminates ground-loop electrostatic interference that can damage devices connected to a sensor.
- Cold Junction Compensation: In this process voltage is added (or subtracted) from the output voltage of the thermocouple. Thus allowing the reference junction to appear at 0°C even if it is not.
Signal Conditioning Systems by Acromag
Metromatics offers a range of signal conditioning systems by Acromag. A few examples of signal conditioners include:
4-20mA Splitters:

The 4-20mA Signal splitters by Acromag receive 4-20mA process current inputs. They also provide two identical isolated 4-20mA output signals. In addition, each channel also operates independently and isolated from others. As a result, there is no interaction between channels. Finally, Galvanic isolation eliminates ground loops, reduces noise and blocks transient signals. Acromag splitters are available in modular, 2-wire loop-powered and 4-wire AC/DC-powered models.
4-20mA Isolators:

The 4-20mA Signal Isolators by Acromag include multi-channel 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire isolators. These are isolated transmitters with AC, DC or loop-powered operation. Also offered is a loop-powered isolator with a panel meter. Optical or galvanic isolation also eliminate ground loop errors, reduce noise and block high voltage transient surges.
Additionally, all Acromag isolators withstand 1500V AC for 60 seconds. They also provide continuous 250V AC or 354V DC common-mode protection of your equipment. Finally, the multi-channel modules reduce cost and save space.
Temperature Transmitters:

Temperature transmitters by Acromag convert thermocouple, RTD, and low-level temperature sensor signals to 4-20mA, 0-10V or other DC voltage/current outputs. Acromag also offer temperature transmitters in head-mount and DIN-rail set-ups. Some temperature transmitters also have software-configured universal inputs. These inputs convert a broad range of temperature sensor and other signals with one unit. Options include: head mount temperature transmitter, DIN-rail temperature transmitter and universal programmable transmitter.
Modbus RTU:

Acromag’s BusWorks 900MB Series is a high-performance collection of analog and discrete I/O modules and relay alarm outputs. Industrial Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) serial transmission mode. These units feature universal input/output ranges and an intelligent microcontroller to provide extreme flexibility and powerful monitoring and control capabilities. These Modbus RTU modules are ideal for a wide variety of distributed I/O applications including data acquisition, control, process monitoring and test & measurement.
You can view more of our signal conditioners range here:
Examples of Signal Conditioners:
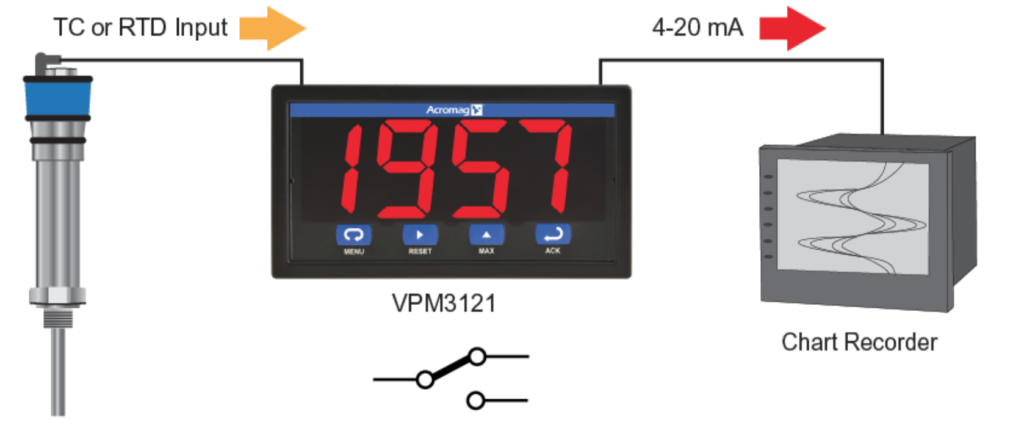
- The Acromag VPM3121 was selected for a manufacturer who needed to monitor their temperature control. This signal conditioner was chosen because of its versatility. It provides warnings/alarms for temperature near fault conditions. It also documents consistent temperatures through the sintering process. In addition to this, the VPM3121 also reads thermocouple signals and displays real time feedback and temperature recordings throughout batch production. Finally, this signal conditioner can also pair with chart recorders. Thanks to this instrument, the manufacturer effectively monitored and maintained temperature control during production. You can read more about this application here.

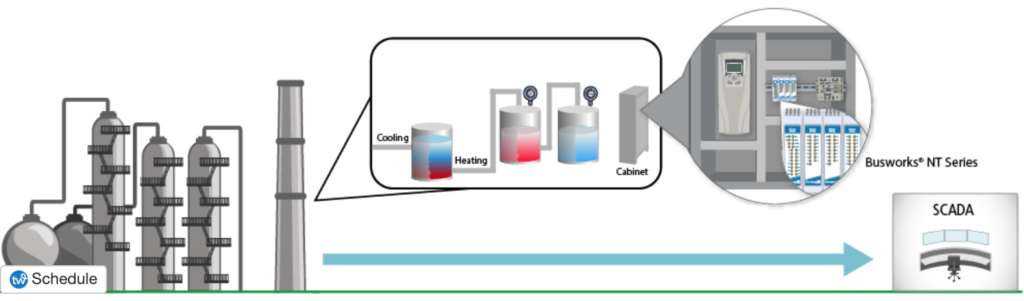
- A chemical manufacturer who had up to 500 temperature measurement points with thermocouple and RTD scattered throughout their process chose Acromag’s BusWorks NT Series of expandable remote I/O to aid in signal conditioning for a project. The manufacturer wanted a cost-efficient solution that didn’t require wires along all of its data points. They opted for an Ethernet signal conditioner. Acromag’s BusWorks NT Series of expandable remote I/O allowed the manufacture to accept a mix of thermocouple and RTD signals. It also allowed the manufacturer to plug up to three expansion units (NTX) of the required I/O in any combination. This solution was both cost effective and allowed the manufacturer to gather data from multiple points. You can read more about this application here.

Learn More
Want to know more? Please contact us here to speak to a member of our team about what signal conditioner is right for you.