Modern platforms increasingly rely on accurate positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) data to operate reliably in dynamic environments. GNSS-derived timing outputs are commonly used for sensor synchronisation, time-aligned data logging, and system coordination within larger platform architectures.
Inertial navigation sensors play a critical role by providing continuous measurements of motion, orientation, and position—particularly when GNSS signals are degraded, unavailable, or unreliable.
VectorNav products assume GNSS availability for absolute position updates, with inertial sensors used to maintain continuity and stability during short GNSS interruptions.
Metromatics supplies VectorNav inertial navigation products in Australia and New Zealand, supporting applications across defence, robotics, marine, test and measurement, and research.
What Are Inertial Navigation Sensors?
Inertial navigation sensors measure how a platform moves and rotates in space. They are commonly used to calculate orientation, velocity, and position in real time.
These sensors typically combine:
- Accelerometers (linear motion)
- Gyroscopes (angular rate)
- Onboard processing and filtering algorithms
When integrated with GNSS, inertial sensors provide robust navigation solutions that continue to operate during short-term GNSS outages or in challenging operating environments.
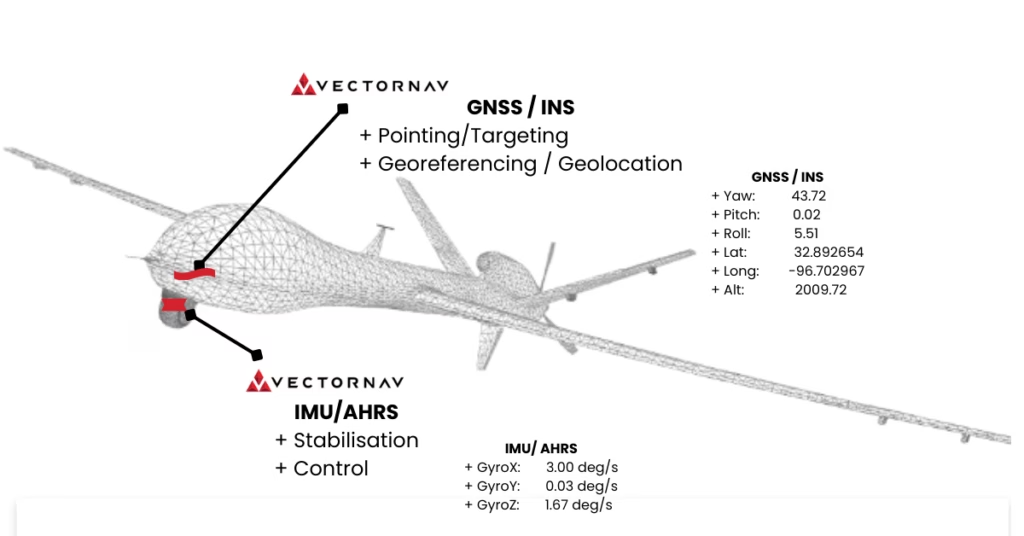
IMU, AHRS and GNSS-INS Explained
Inertial Measurement Units (IMU)
An IMU measures raw acceleration and angular rate along multiple axes. IMUs form the foundation of inertial navigation systems. Commonly integrated into embedded platforms requiring motion data at high update rates. Read more about them here.
Typical IMU outputs include:
- Linear acceleration
- Angular rate
- Calibrated inertial data streams
Our VectorNav Models:
Attitude Heading Reference Systems (AHRS)
An AHRS builds on an IMU by applying onboard filtering to estimate real-time orientation.
AHRS systems provide:
- Roll, pitch and yaw
- Stable orientation outputs
- Simplified integration compared to raw IMUs
AHRS solutions are often used in stabilisation, pointing, and attitude-aware platforms. Learn more about AHRS.
Our VectorNav Models:
GNSS-Aided Inertial Navigation Systems (GNSS/INS)
A GNSS-INS combines inertial sensors with satellite navigation data to deliver a complete navigation solution.
GNSS-INS systems provide:
- Position and velocity from GNSS
- Orientation and motion from inertial sensors
- Continuous navigation estimates during brief GNSS interruptions
By fusing multiple data sources, GNSS-INS solutions outperform standalone GNSS or inertial sensors in dynamic conditions. Learn more about GNSS-INS.
Our Vector Nav Models:
VN-200 GNSS Inertial Navigation System
VN-210 High-Precision GNSS/INS
Dual-Antenna GNSS-INS
Dual-antenna GNSS-INS systems use two GNSS receivers to calculate heading independently of magnetic sensors. This improves heading accuracy and reliability, particularly in environments where magnetic interference is present.
Our VectorNav Models:
VectorNav Inertial Navigation Solutions
VectorNav designs and manufactures MEMS-based inertial navigation products that integrate precision sensors with advanced navigation algorithms. Their product range spans from compact IMU and AHRS devices to fully integrated GNSS-INS and dual GNSS-INS systems.
Key characteristics of VectorNav products include:
- Compact form factors for embedded integration
- Real-time orientation, motion, and navigation outputs
- GNSS-aided and dual-GNSS configurations
- Comprehensive software tools and APIs for development and evaluation
VectorNav solutions are designed to be integrated directly into customer platforms rather than used as standalone navigation appliances.
Typical Outputs from VectorNav Sensors
Depending on configuration, VectorNav systems can output:
- Accelerometer and gyroscope data
- Attitude (roll, pitch, yaw)
- Position and velocity
- GNSS-derived timing
- Quaternions and direction cosine matrices
These outputs support downstream processing, autonomy stacks, data acquisition systems, and control systems.
Applications
VectorNav inertial navigation sensors are used in a wide range of applications, including:
Defence & Aerospace
In defence applications, VectorNav products are commonly used for vehicle orientation reference, navigation aiding within mission systems, motion compensation, and test or evaluation instrumentation.
- Ground vehicles and aerospace platforms
- Navigation and orientation for mission systems
- PNT subsystems within larger vehicle architectures
Robotics & Autonomous Systems
- UAVs, UGVs and USVs
- Sensor fusion for autonomy and control
- Navigation in dynamic or GNSS-challenged environments
Marine & Survey
- Motion reference for survey and mapping
- Vessel attitude and heading measurement
- Georeferencing and navigation support
Test & Measurement & Rail Applications
- Vehicle dynamics testing
- Motion truth reference data
- Time-aligned data acquisition
Research & Development
- University and laboratory research
- Algorithm development and validation
- Navigation and sensor fusion experimentation
Software, Tools and Integration
VectorNav provides configuration and monitoring software, along with software libraries for common programming environments. These tools support system setup, data visualisation, and integration into customer software stacks.
Comprehensive documentation and application resources are available to support evaluation and deployment.
Final navigation performance depends on system-level factors such as antenna placement, vehicle dynamics, environmental conditions, and integration with external aiding sources.
Local Support from Metromatics
As the Australian and New Zealand distributor for VectorNav, Metromatics provides:
- Local sales and technical support
- Application scoping and product selection assistance
- Integration support alongside data acquisition and embedded computing systems
- Ongoing support throughout the project lifecycle
Our role is to help customers select the most suitable inertial navigation solution for their specific application.
Not sure which inertial navigation sensor you need?
👉 Request a VectorNav product recommendation
👉 Talk to our team about your application
👉 Request pricing or lead-time information